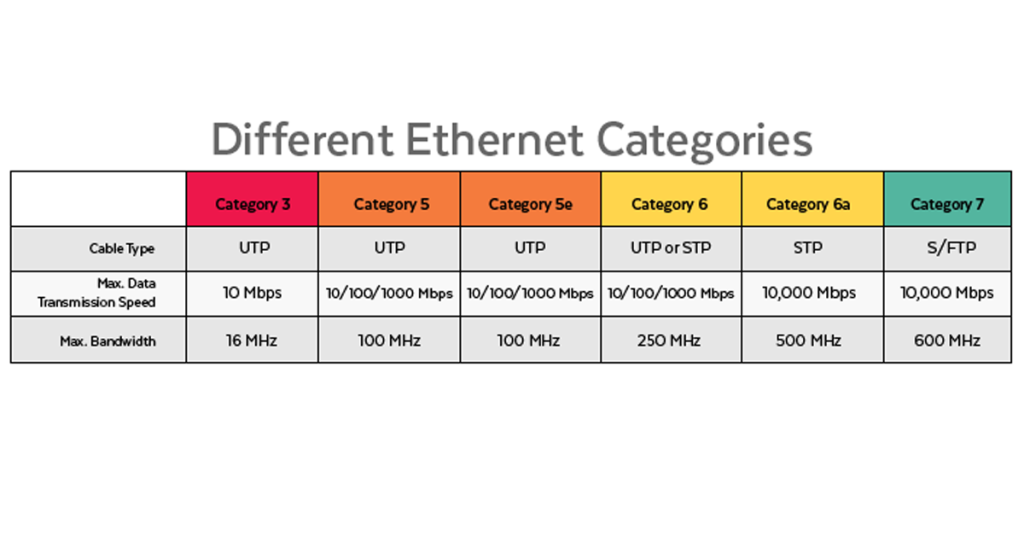
In the world of networking, Ethernet cables play a crucial role in connecting devices and facilitating data transfer. With various categories available, such as Cat3, Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8, it can be challenging to decipher which type is best suited for specific applications. Each category comes with its own set of characteristics, capabilities, and limitations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the differences between these Ethernet cable categories to help you make informed decisions when setting up your network infrastructure.
- Cat3:
- Cat3 cables were popular in the early days of Ethernet networking.
- They are capable of transmitting data at speeds up to 10 Mbps.
- Cat3 cables are mostly obsolete for modern networking needs and are primarily used for telephone wiring.
- Cat5:
- Cat5 cables support speeds of up to 100 Mbps and are suitable for basic networking requirements.
- They are commonly used in home networks and small businesses.
- Cat5 cables consist of four twisted pairs of copper wire.
- Cat5e (Enhanced):
- Cat5e cables are an improvement over Cat5 cables, providing better performance and less interference.
- They support speeds of up to 1 Gbps (1000 Mbps) and are backward compatible with Cat5 cables.
- Cat5e cables are widely used in both residential and commercial environments.
- Cat6:
- Cat6 cables offer higher performance compared to Cat5e cables.
- They support speeds of up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances (up to 55 meters).
- Cat6 cables are suitable for demanding applications such as data centers, server rooms, and high-speed LANs.
- Cat6a (Augmented):
- Cat6a cables are an enhancement over Cat6 cables, featuring better insulation and performance.
- They support higher data transmission rates of up to 10 Gbps over longer distances (up to 100 meters).
- Cat6a cables are ideal for applications requiring high-speed data transfer, such as multimedia streaming and IP video surveillance.
- Cat7:
- Cat7 cables are designed to operate at frequencies of up to 600 MHz.
- They support data transfer rates of up to 10 Gbps over distances of up to 100 meters.
- Cat7 cables feature individually shielded twisted pairs (S/FTP) to minimize crosstalk and interference.
- Cat8:
- Cat8 cables are the latest addition to the Ethernet cable family, offering blazing-fast speeds and exceptional performance.
- They support data transfer rates of up to 25 Gbps or even 40 Gbps over distances of up to 30 meters.
- Cat8 cables are ideal for data center environments, high-performance computing, and future-proofing network infrastructure.
In summary, the choice of Ethernet cable category depends on the specific requirements of your networking setup. For basic home or small office networks, Cat5e cables may suffice, offering a balance of performance and cost-effectiveness. However, for more demanding applications requiring higher speeds and greater reliability, upgrading to Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, or Cat8 cables may be necessary. It’s essential to consider factors such as data transfer rates, cable length, and environmental conditions when selecting the appropriate Ethernet cable for your network.
By understanding the differences between Cat3, Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, and Cat8 cables, you can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance and efficiency in your network infrastructure. Whether you’re setting up a home network, a business LAN, or a data center, choosing the right Ethernet cables is crucial for achieving reliable and high-speed connectivity.

This post is an excellent guide for understanding the different types of Ethernet cables and their specific uses. The detailed breakdown of each category— from CAT3 all the way to CAT8—helps clarify the strengths and limitations of each type, making it much easier to choose the right cable for any networking needs. I especially appreciate the way the post explains the technological advancements in cable performance, from speed to bandwidth. It’s an invaluable resource for anyone looking to optimize their network setup or just better understand how Ethernet cables work!